A Guide to the Business Analysis Body of Knowledge (BABOK® Guide) is the standard for the practice of business analysis and is for professionals who perform business analysis tasks. Recognized globally as the standard of business analysis, it guides business professionals within the six core knowledge areas, describing the skills, deliverables, and techniques that business analysis professionals require to achieve better business outcomes.
Generic Business Analysis job descriptions
Generic job/role descriptions (referencing BABOK v3 and SFIA v8) for the following:
- Business Analysis Practice Lead
- Senior Business Analyst
- Business Analyst
- Trainee/Apprentice Business Analyst
The template describes.
- Job purpose
- Job responsibilities
- Minimum requirements for the role
- Education and qualifications
- Mapping to BABOK knowledge areas, SFIA skills and levels
- Illustrative mapping to organisational behaviours/values
Download
- Generic business analysis job/role descriptions.docx
- Generic business analysis job/role descriptions.pdf
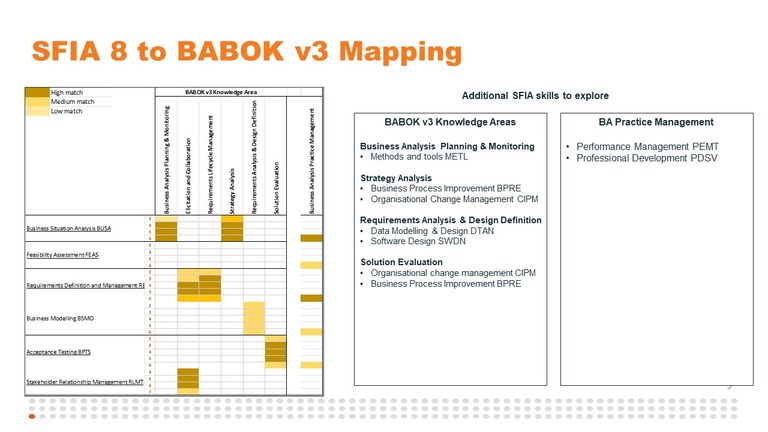
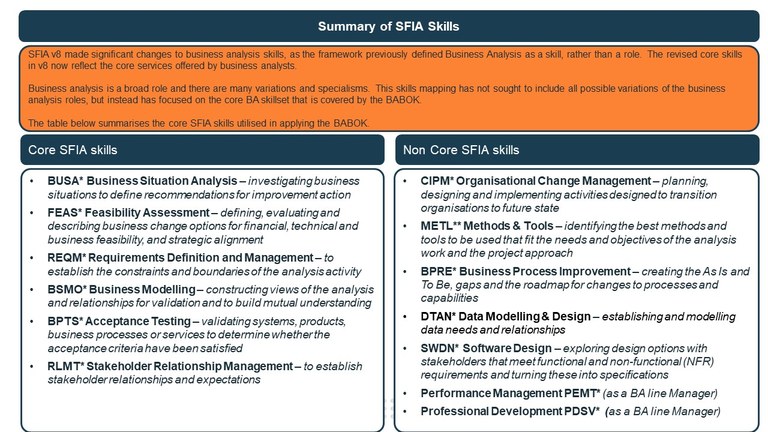
Listing of all the SFIA skills mapped from the BABOK
You can click on each skill name for full skill level descriptions, guidance notes.
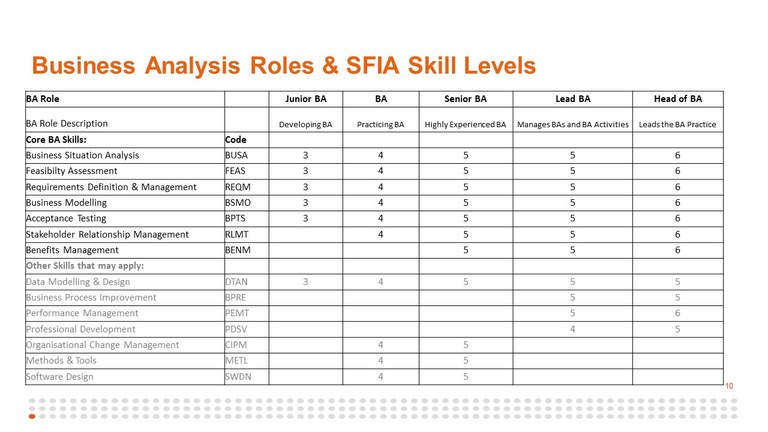
| SFIA skill name | Levels |
| Core Business Analyst skills | Business situation analysis BUSA | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
| Feasibility assessment FEAS | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
| Requirements definition and management REQM | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
| Business modelling BSMO | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
| Acceptance testing BPTS | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
| Stakeholder relationship management RLMT | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| Benefits management BENM | 5 | 6 |
| Other skills that may apply | Data modelling and design DTAN | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| Business process improvement BPRE | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| Organisational change management CIPM | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
| Methods and tools METL | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
| Software design SWDN | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
| For people managers and BA practice leaders | Performance management PEMT | 4 | 5 | 6 |
| Professional development PDSV | 4 | 5 | 6 |
Background
- The BABOK – Business Analysis Body of Knowledge is the trusted reference guide for Business Analysts developed by the International Institute of Business Analysis – IIBA
- In Q1 2021 - the IIBA UK mapped SFIA version 7 skills to BABOK knowledge areas (KAs)
- In Q1 2023 - IIBA UK volunteers updated the skills mapping to align to SFIA version 8
- The SFIA skills were selected on the basis that they were the skills needed to apply the knowledge described in the BABOK (KAs)
- For simplicity - SFIA levels were not included in the mapping. However, the SFIA 8 mapping has suggested appropriate SFIA skill levels for the Business Analysis job family and career path.
- If you are interested - please get in touch - [email protected]
Acknowledgement - Selected extracts from A Guide to the Business Analysis Body of Knowledge® (BABOK® Guide) Version 3.0, IIBA.
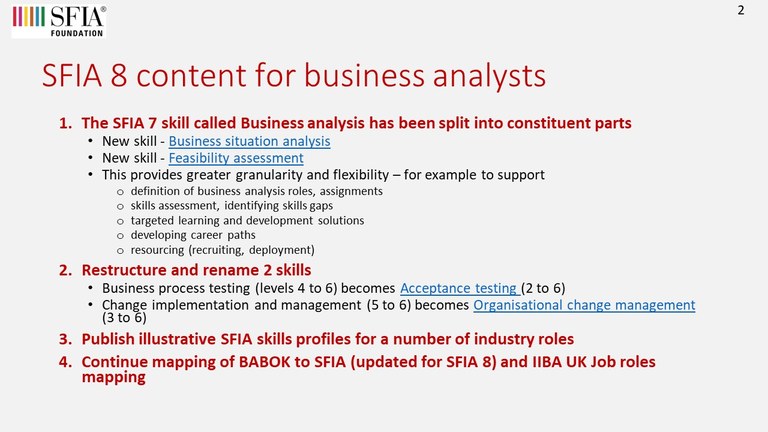
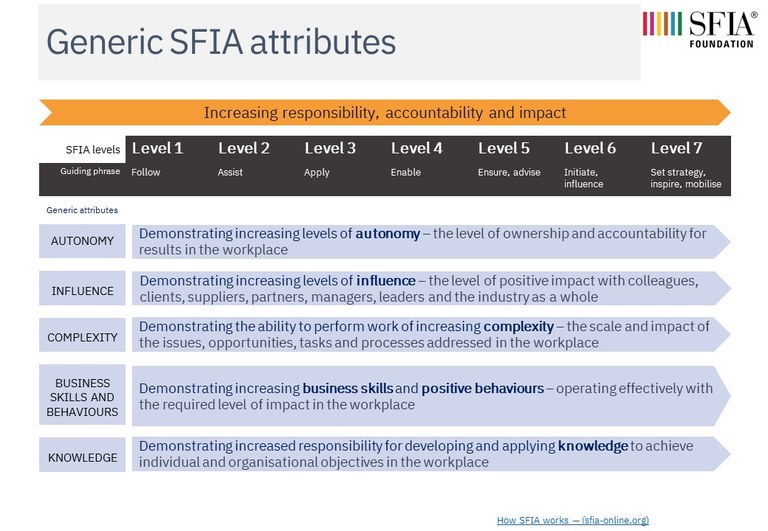
SFIA 8 provided a number of enhancements to support business analysis -related skills
- If you are not familiar with the SFIA framework - you can get an overview of the guiding principles of SFIA.

The Framework of the BABOK
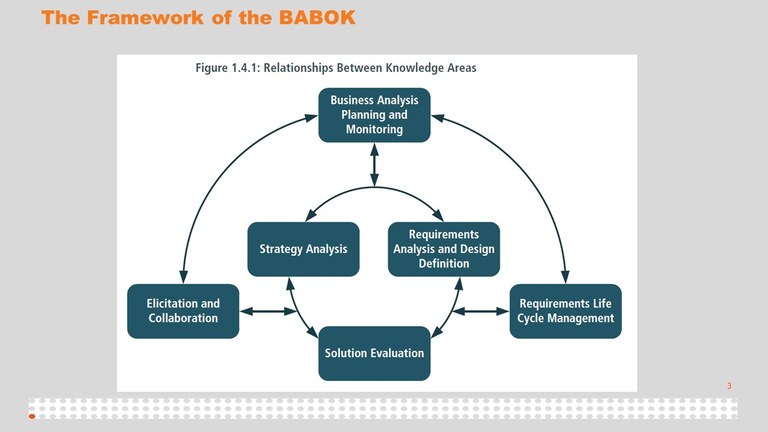
Click image to see the relationship between the BABOK knowledge areas.
Approach used to develop the mapping
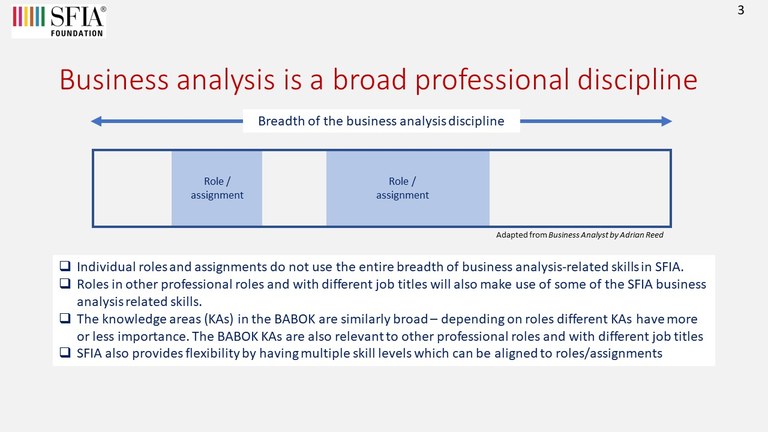
Each of the knowledge areas in the BABOK were analysed to determine the related SFIA skills. When considering the mapping, the focus was on the key accountabilities of the role, as opposed to discrete tasks that may be performed. It is understood that the role of a business analyst can differ depending on the organisational need and role specialism. This mapping is not intended to cover all possible variations or specialisms of business analysis roles.
To help adoption - these were further refined into 2 groups.
- SFIA skills most likely to be used and which are considered core business analyst skills
- Other SFIA skills that may be used, depending on organisation/role context
Business analysis planning & monitoring
Topics.
- Planbusiness analysis approach: includes selecting/ creating methodology & planning individual activities, tasks, & deliverables
- Planstakeholder engagement - includes understanding the stakeholders, theirs and our mutual needs and the best way to collaborate
- Plan business analysis governance - includes plans for decision making & working within established governance frameworks such as for risk
- Plan business analysis information management - setting out how the information captured by the BA will be stored, used and integrated with other information
- Identify business analysis performance improvements - to identify how commitments will be met and how continuous learning opportunities will be realised
Elicitation and Collaboration
Topics.
- Prepare for elicitation - includes conducting any research & building a shared set of expectations with stakeholders
- Conduct elicitation - includes the work to understand stakeholder needs and to identify potential solutions
- Confirm elicitation results - includes cross referencing with other artefacts and ensuring stakeholders have a shared understanding of the outcomes of elicitation
- Communicate business analysis information - presenting information back to stakeholders in a digestible manner and a timely way
- Manage stakeholder collaboration - to engage stakeholders appropriately such that desired analysis outcomes can be reached
Requirements Lifecycle Management
Topics.
- Trace requirements - includes analysis & modelling of relationships between requirements & artefacts, to improve clarity and understanding
- Maintain requirements - ensures requirements & designs are accurate, current & reusable
- Prioritise requirements - ensures work can be scoped and adjustments made as and when priorities or criteria for inclusion change
- Assess requirements changes - implementation of controls to ensure there is a stable baseline to the requirements
- Approve requirements - ensures relevant stakeholders give their support and buy in to the products of the requirements activities
Strategy Analysis
Topics.
- Analyse current state - sets the baseline and context for change
- Define future state - sets the objectives of the change and clarifies which parts of the enterprise will need to change
- Assess risks - ensures challenges ahead are identified and plans made to deal with these appropriately
- Define change strategy - implementation of controls to ensure there is a stable baseline to the requirements

Requirements Analysis & Design Definition
Topics.
- Specify and model requirements - using information elicited to build requirements from which to move forwards with the change
- Verify requirements - ensuring the requirements are specified to the required level of detail and completeness
- Validate requirements - ensuring these are accepted as representative of the stakeholders needs
- Define requirements architecture - ensures the various views, models and or catalogues/ backlogs created form a coherent whole/ a complete story
- Define solution options - sets out potential ways forwards
- Analyse potential value & recommend solution - provides relevant information to support decision making and pointers to the way forwards
Solution Evaluation
Topics.
- Measure solution performance - design and carry out the measure against enterprise goals and objectives
- Analyse performance measures - examines findings to determine whether the solution is meeting the business needs
- Assess solution limitations - looks for underlying causes as to why the solution is not meeting business needs
- Assess enterprise limitations - looks for underlying causes as to what is preventing the enterprise from realising the full potential of the solution
- Recommend actions to increase solution value - exactly as it sounds
Listing of all the SFIA skills mapped from the BABOK
Click on each skill name for full descriptions including skill level descriptions.











